分享:基于應(yīng)變匹配的高性能金屬納米復(fù)合材料研究進(jìn)展
中國石油大學(xué)(北京)理學(xué)院 北京 102200
摘要
納米線具有超高強(qiáng)度及超大彈性應(yīng)變,以其增強(qiáng)的復(fù)合材料被預(yù)期具有超常力學(xué)性能,然而,已有研究結(jié)果一直“令人失望”。其原因是納米線的超常力學(xué)性能未能在復(fù)合材料中體現(xiàn)。基于對位錯(cuò)滑移型金屬基體中的位錯(cuò)與納米線界面交互作用是“失望”之源的猜想,提出采用點(diǎn)陣切變型金屬的切應(yīng)變與納米線的彈性應(yīng)變相匹配的設(shè)計(jì)概念,選擇納米線Nb/NiTi 記憶合金等體系,證實(shí)了納米線(帶、粒子)的超常力學(xué)性能得以在復(fù)合材料中體現(xiàn),使復(fù)合材料具備超常力學(xué)性能成為現(xiàn)實(shí)。此外,還發(fā)現(xiàn)上述突破可引發(fā)復(fù)合材料呈現(xiàn)超常力學(xué)性能的新機(jī)制(大應(yīng)力耦合效應(yīng)等)。據(jù)此設(shè)計(jì)的Nb納米線/NiTi 記憶合金復(fù)合材料兼具:彈性應(yīng)變極限大于6%,彈性模量低于28 GPa,屈服強(qiáng)度高達(dá)1.65 GPa。
關(guān)鍵詞:
納米線具有超大彈性應(yīng)變極限(4%~7%)及超高屈服強(qiáng)度[1,2,3,4],材料科學(xué)家預(yù)見,以其增強(qiáng)的復(fù)合材料應(yīng)具有超常性能。然而,研究[5]表明,納米線的超常力學(xué)性能不能在復(fù)合材料中體現(xiàn)(彈性應(yīng)變極限小于1.8%),使大塊復(fù)合材料未呈現(xiàn)預(yù)期的超常力學(xué)性能,此“超常力學(xué)性能未能從納米走向宏觀”現(xiàn)象被喻為“死亡之谷”。諸多學(xué)者[5,6,7]將其原因歸結(jié)為:(1) 納米線在基體中分散不均勻,且其難以沿受載方向定向分布;(2) 納米線與基體界面結(jié)合強(qiáng)度低。近年來,經(jīng)過諸多努力已成功制備了納米線在基體中分散均勻、沿受載方向定向分布,且兩者界面強(qiáng)度高的復(fù)合材料(如Nb納米線/Cu原位復(fù)合材料[8,9,10,11])。然而,復(fù)合材料中納米線仍未能體現(xiàn)超常力學(xué)性能。對此,Dzenis[5]指出,材料科學(xué)家曾預(yù)見,由于納米線具有超高強(qiáng)度,其增強(qiáng)復(fù)合材料應(yīng)具有超常性能,然而,已有研究結(jié)果均令人失望;雖然一直在進(jìn)行大量研究,然而前景似乎比以前更加渺茫;納米線的本征超大彈性應(yīng)變/超高強(qiáng)度在復(fù)合材料中不能被實(shí)現(xiàn),且目前尚不清楚這種實(shí)現(xiàn)是否可能。
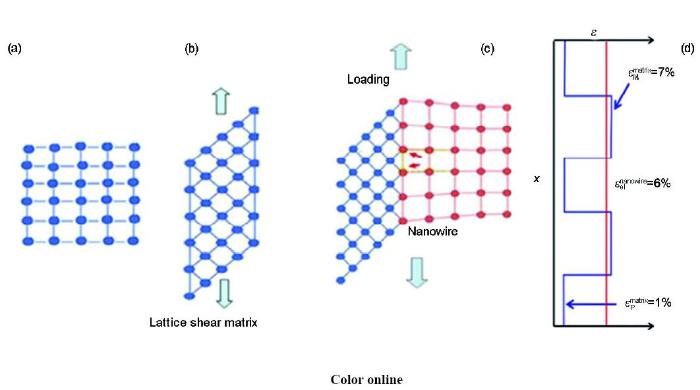
位錯(cuò)滑移型金屬在受載發(fā)生初始彈性變形(應(yīng)變較小)之后的塑性變形過程中,位錯(cuò)將由其內(nèi)部(圖1a)滑移至表面而形成Burgers矢量臺階(圖1b中箭頭所示),若納米線與此基體相鄰接,則在基體/納米線的界面處會形成約100%應(yīng)變的原子尺度高應(yīng)力集中(圖1c),導(dǎo)致納米線在此高應(yīng)力集中處提前發(fā)生塑性變形,而不能再現(xiàn)其超常力學(xué)性能,圖1d顯示位錯(cuò)處的輸出應(yīng)變接近100%,而非位錯(cuò)處的輸出應(yīng)變(初始彈性應(yīng)變)僅為0.2%。
圖1 位錯(cuò)滑移型金屬基體及其與納米線匹配的二維點(diǎn)陣示意圖,當(dāng)位錯(cuò)(兩根位錯(cuò))滑移至界面時(shí)位錯(cuò)滑移基體輸出應(yīng)變的分布示意圖
Fig.1 Two-dimension lattice schematic of the strain match between the nanowire and the dislocation slip matrix(a) matrix before dislocation slip(b) formed Burgers step (red line) after dislocation slip(c) atomic-scale high stress concentration (dotted circle) was generated when the dislocation moves to the interface between the nanowire and the matrix(d) schematic of the strain (ε) distribution when the dislocation slips to the interface, which shows the inelastic shear strain of matrix (
另外有一類金屬材料,在受載過程中發(fā)生點(diǎn)陣切變變形(如應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體相變變形或去孿晶變形),見圖2a和b,此類變形機(jī)制為原子集體發(fā)生切變變形,且此切變應(yīng)變(約7%)遠(yuǎn)高于位錯(cuò)滑移金屬的初始彈性應(yīng)變,與納米線的超大彈性應(yīng)變(約6%,圖2c和d)相匹配(簡稱“應(yīng)變匹配”)。圖2d顯示母相區(qū)域的輸出應(yīng)變?yōu)?%,馬氏體區(qū)域的輸出應(yīng)變?yōu)?%,此應(yīng)變與納米線的彈性應(yīng)變(6%,紅線)相匹配。若將此類點(diǎn)陣切變變形機(jī)制的金屬作為基體,與納米線相鄰接,則在受載變形過程中,在基體/納米線界面處不存在原子尺度的高應(yīng)力集中(圖2c),從而避免納米線提前發(fā)生塑性變形,使納米線再現(xiàn)其本征超常力學(xué)性能,可望跨越“死亡之谷”。
圖2 點(diǎn)陣切變基體與納米線匹配的二維點(diǎn)陣及應(yīng)變分布示意圖,基體發(fā)生應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體變形(馬氏體和母相共存)過程中點(diǎn)陣切變基體輸出應(yīng)變的分布示意圖
Fig.2 Two-dimension lattice schematic of the strain match between the nanowire and the lattice shear matrix(a) matrix before lattice shear(b) matrix after lattice shear(c) interface between the nanowire and the matrix after lattice shear, showing no atomic-scale high stress concentration(d) schematic of the strain distribution when the matrix experiences the stress induced martensitic transformation, which shows the elastic strain of matrix (
依據(jù)上述思想,我們采用真空感應(yīng)熔煉獲得成分為Ti39Ni41Nb20 (原子分?jǐn)?shù),%)的Nb-NiTi共晶合金錠,通過常規(guī)的鍛造及拔絲獲得Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金原位復(fù)合材料絲材(圖3a[12]),其中,Nb納米線沿絲軸向均勻、彌散分布在NiTi基體中(圖3b和c[12])。采用電解萃取法去除NiTi基體,可發(fā)現(xiàn)Nb納米線簇長度大于120 mm (圖3d和e[12]),直徑約為60 nm (圖3f[12])。
圖3 Nb納米線/NiTi基體復(fù)合材料絲材及其微觀組織[
Fig.3 The macro and micro images of the nanowire Nb/NiTi composite[
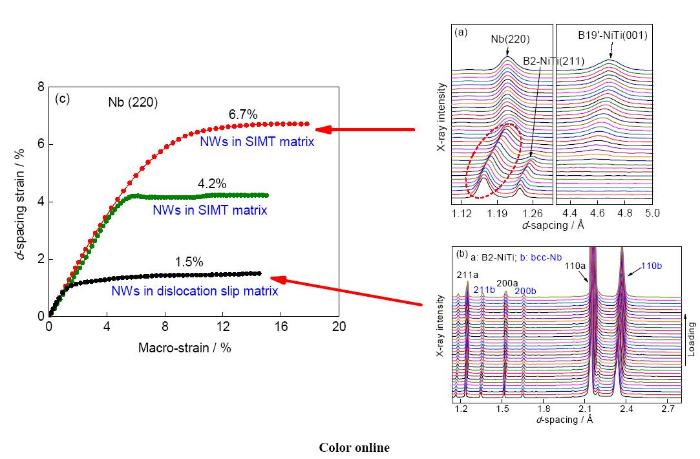
采用高能同步輻射X射線衍射技術(shù)跟蹤了Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料絲材在加載過程中的微觀結(jié)構(gòu)演變(圖4a和b[12]),并根據(jù)衍射譜線計(jì)算了Nb納米線晶格應(yīng)變(代表彈性應(yīng)變)與外加應(yīng)變的關(guān)系(圖4c[12])。可見,在NiTi基體發(fā)生應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體相變變形過程中,Nb納米線呈現(xiàn)的彈性應(yīng)變極限為4.2%或6.7%。對于同一樣品,若使NiTi基體發(fā)生位錯(cuò)滑移變形,Nb納米線僅呈現(xiàn)1.5%的彈性應(yīng)變(圖4c[12])。這證實(shí)了在NiTi基體發(fā)生馬氏體相變(點(diǎn)陣切變)變形過程中,Nb納米線超大彈性應(yīng)變得以再現(xiàn)。
圖4 Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金樣品在原位拉伸過程中的高能同步輻射XRD譜以及Nb納米線的晶格應(yīng)變曲線[
Fig.4 The high energy synchrotron XRD of the nanowire Nb/NiTi sample during tensile test and the evolution of the lattice strain with respect to the applied strain of Nb nanowire[
采用原位拉伸同步輻射高能X射線進(jìn)行了大量測試實(shí)驗(yàn),發(fā)現(xiàn)對于不同直徑(10~60 nm)的Nb納米線,在NiTi基體發(fā)生應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體相變過程中,其呈現(xiàn)的彈性應(yīng)變極限在4%~7%范圍內(nèi)(圖5(2)[12]),與以往報(bào)道的單體態(tài)納米線彈性應(yīng)變極限相當(dāng)(見圖5(3)[12]),遠(yuǎn)高于位錯(cuò)滑移基體中納米線的彈性應(yīng)變極限(見圖5(1)[12]),這充分證明了我們提出的“應(yīng)變匹配”新設(shè)計(jì)概念,使納米線超大彈性應(yīng)變得以再現(xiàn),跨越了長期困擾材料科學(xué)家的“死亡之谷”[5]。
圖5 Nb納米線在位錯(cuò)滑移型金屬基體中在應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體相變NiTi基體中的彈性應(yīng)變極限,與文獻(xiàn)報(bào)道的多種自由態(tài)納米線的彈性應(yīng)變極限的比較[
Fig.5 Comparison of the elastic strain limits of Nb nanowires embedded in the matrix deforming by dislocation slip (1), Nb nanowires embedded in the matrix deforming by SIMT (2), and some freestanding nanowires (3)[
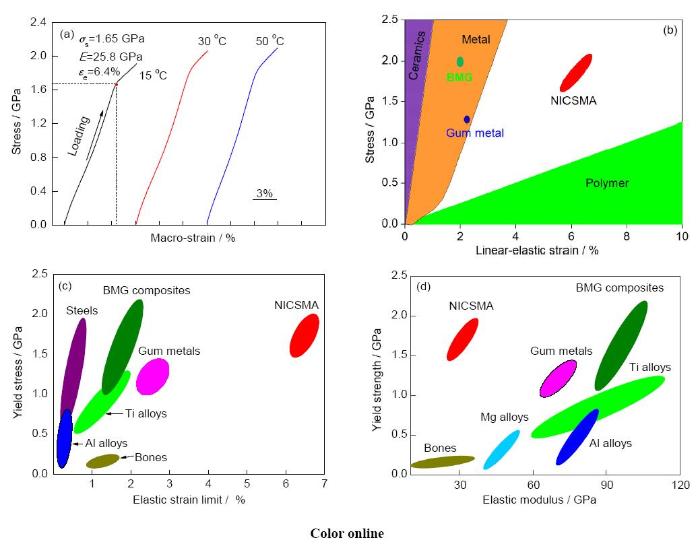
基于上述突破,研發(fā)的Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金基體復(fù)合材料呈現(xiàn)超常力學(xué)性能(圖6a[12]),其中,彈性應(yīng)變極限大于6%,遠(yuǎn)大于大塊金屬材料(圖6c[12]);彈性模量低于28 GPa,遠(yuǎn)低于以往報(bào)道的大塊金屬材料,與人骨的彈性模量相當(dāng)(圖6d[12]);屈服強(qiáng)度大于1.65 GPa,彈性儲能高達(dá)50 J/cm3 (是彈簧鋼的10倍),表明Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料兼具超大彈性應(yīng)變、低彈性模量及高屈服強(qiáng)度的綜合性能,填補(bǔ)了三大類工程材料力學(xué)性能的挑戰(zhàn)區(qū)(圖6b[12])。
圖6 Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料(NICSMA)的拉伸應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變曲線、NICSMA性能占據(jù)三大類工程材料性能挑戰(zhàn)區(qū)、NICSMA與其它金屬材料屈服強(qiáng)度和彈性應(yīng)變極限的比較、與其它材料屈服強(qiáng)度和彈性模量的比較[
Fig.6 Tensile stress-strain curves of the nanowire in situ composite with shape memory alloy (NICSMA) composite (εe—elastic limit, σs—yield strength, E—elastic modulus) (a), comparison of strengths and elastic strains of ceramics, metals, polymers and our composite (marked by NICSMA) (b), comparison of the yield strengths and elastic strain limits of different materials (c), comparison of the yield strengths and Young's moduli of different materials (d)[
單體態(tài)納米線(各區(qū)域橫截面積相同)在受外載發(fā)生彈性變形過程中,其彈性應(yīng)變分布均勻,且變形速率受外載控制。本研究發(fā)現(xiàn),相變基體中納米線超大彈性變形與單體態(tài)不同,其受基體的馬氏體相變變形控制,呈現(xiàn)瞬時(shí)性與局域性。
最初,我們曾認(rèn)為,相變基體中納米線的超大彈性變形與單體態(tài)納米線類似[12],我們進(jìn)一步推測,這是由于基體發(fā)生均勻型應(yīng)力誘發(fā)相變所致,該均勻型相變造成納米線與基體的兩相(母相+馬氏體相)鄰接,而馬氏體相的輸出應(yīng)變(約6%)遠(yuǎn)大于母相的輸出應(yīng)變(約1%)。由于同步輻射高能X射線束尺寸(0.4 mm×0.4 mm)遠(yuǎn)大于此兩相的尺度,因此,其測試結(jié)果為納米線彈性應(yīng)變的平均值,尚不能揭示相變基體中納米線彈性變形的本質(zhì)行為。
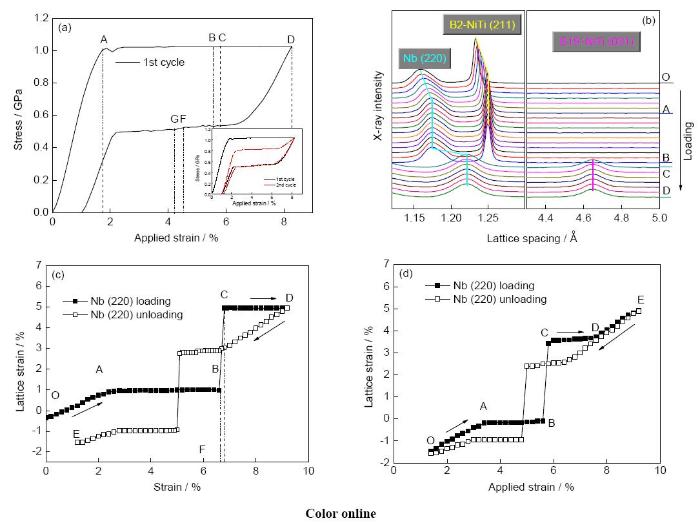
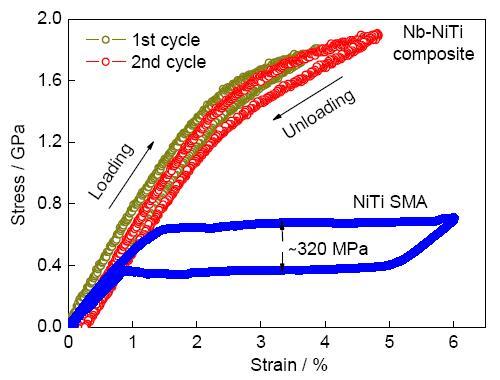
為使高能X射線探測到與單一馬氏體相區(qū)域鄰接納米線的彈性變形行為,我們通過調(diào)整納米線比例,使基體發(fā)生Lüders bands型相變(高能X射線探測區(qū)的基體由單一相組成)。圖7a[13]為發(fā)生Lüders bands型相變樣品循環(huán)加卸載的應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變曲線。結(jié)果發(fā)現(xiàn),伴隨母相轉(zhuǎn)變?yōu)轳R氏體相(圖7b[13]中加載由B→C,B2-NiTi (211)峰消失,B19'-NiTi (001)峰出現(xiàn)),Nb納米線的彈性應(yīng)變由1.4%跳躍式增加到5.2% (圖7c[13]中B→C),其增量(3.8%)是外加應(yīng)變增量(0.2%)的19倍,這說明納米線的超大彈性變形與基體的相變變形同步。證明了納米線的彈性變形受基體的馬氏體相變變形(馬氏體片的形核與長大在小于10-3 s內(nèi)完成)控制,呈現(xiàn)瞬時(shí)性與局域性。
圖7 Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金樣品的拉伸循環(huán)應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變曲線、樣品在第一次加載過程中的同步輻射高能XRD譜、納米線在第一次加卸載過程中的晶格應(yīng)變曲線、納米線在第二次加卸載過程中的晶格應(yīng)變曲線[
Fig.7 The cyclic tensile stress-strain curve of the nanowire in situ composite with shape memory alloy sample (a), evolution of the diffraction peaks for Nb (220), B2-NiTi (211) and B19'-NiTi (001) planes perpendicular to the loading direction during loading (b), evolution of the lattice strain with respect to the applied strain for Nb (220) plane perpendicular to the loading direction during the first cycle (c), evolution of the lattice strain with respect to the applied strain for Nb (220) plane perpendicular to the loading direction during the second cycle (d)[
我們還發(fā)現(xiàn),當(dāng)基體的相變應(yīng)變大于(過匹配)或小于(欠匹配)納米線彈性應(yīng)變時(shí),納米線呈現(xiàn)不同的超大彈性變形特征。當(dāng)基體相變應(yīng)變“過”匹配于納米線彈性應(yīng)變極限時(shí),在受載過程中,納米線發(fā)生塑性變形(圖7c[13])。當(dāng)基體相變應(yīng)變“欠”匹配于納米線彈性應(yīng)變時(shí),在受載過程中,納米線不發(fā)生塑性變形(圖7d[13])。
如前所述,使用原位拉伸同步輻射高能X射線測試納米線超大彈性應(yīng)變,為進(jìn)一步提供微觀實(shí)驗(yàn)證據(jù),采用原位拉伸透射電鏡(TEM)直接觀察到納米線彈性應(yīng)變。
首先,采用TEM觀察了Nb納米線體積分?jǐn)?shù)分別為10%和20%的NiTi基體復(fù)合材料微觀組織,由于2種樣品的電子衍射譜中B2-NiTi<110>衍射強(qiáng)度在0°~360°范圍分布均勻,而納米線Nb<110>衍射強(qiáng)度主要沿軸向分布,說明NiTi基體幾乎不存在織構(gòu),而Nb納米線存在較強(qiáng)的<110>絲織構(gòu),見圖8a和b[14]。還可關(guān)注到:在2種樣品中,Nb納米線均平行于軸向排列,其中,前者樣品中Nb納米線的直徑為10~15 nm,略小于后者Nb納米線的直徑(20~30 nm),見圖8c和f [14];2種樣品中NiTi基體晶粒細(xì)小,直徑均為20 nm。從圖8g和h[14]可見,2種樣品中Nb納米線在視野范圍內(nèi)呈單晶態(tài),Nb納米線與NiTi基體呈良好的半共格界面。
圖8 Nb納米線體積分?jǐn)?shù)分別為10%和20%的NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料絲材的電子顯微分析[
Fig.8 TEM analyses of two NiTi shape memory alloy composites with 10% and 20% volume fraction Nb nanowire[
圖9[15]是采用原位拉伸TEM (可雙傾)觀察的復(fù)合材料中Nb納米線的彈性變形行為,發(fā)現(xiàn)在原位拉伸過程中,Nb納米線的彈性應(yīng)變呈現(xiàn)不均勻性。在鄰接馬氏體片區(qū)域的彈性應(yīng)變高達(dá)約8% (圖10[15]),遠(yuǎn)高于以往報(bào)道的納米線彈性應(yīng)變,接近納米線理論彈性應(yīng)變極限。
圖9 在原位TEM拉伸過程中Nb納米線的彈性變形行為[
Fig.9 TEM study of lattice strain matching between Nb nanowires and the NiTi matrix[
圖10 包含M1和M3馬氏體板條區(qū)域的高分辨像及Nb納米線中晶格應(yīng)變的變化規(guī)律[
Fig.10 HRTEM image of the region covering martensite plates M1 and M3. The interplanar spacing variation was calculated at an interval of seven (110)Nb planes (a) and distribution of the lattice strain as a function of distance from the start plane (b)[
上述采用“應(yīng)變匹配”的新設(shè)計(jì)概念,使馬氏體相變基體中納米線的超常力學(xué)性能得以再現(xiàn),跨越了“死亡之谷”。進(jìn)一步研究[12,16]表明,此設(shè)計(jì)概念還普適于:相變基體中的納米帶與納米粒子;去孿晶變形(點(diǎn)陣切變)基體。
圖11a和b[12]分別是Nb納米帶/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料絲的橫截面和縱截面的STEM像。可見,均勻分布在NiTi基體中Nb元素以納米帶形式存在,其平均厚度約為20 nm,寬度主要集中在60~200 nm。原位拉伸同步輻射高能X射線衍射結(jié)果表明(圖11c[12]),在基體發(fā)生應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體相變過程中,Nb納米帶呈現(xiàn)的彈性應(yīng)變高達(dá)6.5%,遠(yuǎn)大于基體發(fā)生位錯(cuò)滑移過程中納米線的彈性應(yīng)變(1.5%),證實(shí)了“應(yīng)變匹配”的設(shè)計(jì)概念普適于納米帶。
圖11 Nb納米帶/NiTi基體復(fù)合材料絲的橫截面和縱截面的STEM照片、垂直于加載方向的Nb (220)晶面的晶格應(yīng)變與施加應(yīng)變的關(guān)系曲線(插圖為樣品在室溫下的拉伸應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變曲線)[
Fig.11 STEM images of a cross-section (a) and a longitudinal-section (b) of a ribbion Nb/NiTi composite, evolution of the d-spacing strain with respect to the applied macroscopic strain for the Nb (220) plane perpendicular to the loading direction (Inset shows the stress-strain curve of the sample at room temperature) (c)[
通過熱處理使復(fù)合材料絲材中Nb粒子的平均直徑為120 nm。原位同步輻射高能X射線衍射拉伸結(jié)果表明,在B2-NiTi基體發(fā)生Lüders bands型應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體相變過程中,Nb納米粒子呈現(xiàn)的彈性應(yīng)變達(dá)到2%。而在B2-NiTi基體發(fā)生了位錯(cuò)滑移塑性變形過程中,Nb粒子呈現(xiàn)的彈性應(yīng)變?yōu)?.83%。說明相變基體中納米粒子的彈性應(yīng)變明顯高于位錯(cuò)滑移基體中納米粒子的彈性應(yīng)變,證實(shí)了“應(yīng)變匹配”的設(shè)計(jì)概念普適于納米粒子。
通過化學(xué)成分設(shè)計(jì),使NiTi基體處于馬氏體(內(nèi)部為孿晶)狀態(tài),同步輻射檢測發(fā)現(xiàn),隨著Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料樣品拉伸應(yīng)變的增加,NiTi基體的馬氏體發(fā)生去孿晶(圖12b[16]);采用TEM觀察證明了在拉伸(8.7%)過程中馬氏體態(tài)NiTi基體發(fā)生了去孿晶變形(圖12c[16]),且在此過程中,Nb納米線呈現(xiàn)的彈性應(yīng)變達(dá)到5.6% (圖12a[16]),遠(yuǎn)高于位錯(cuò)滑移型金屬基體中Nb納米線的彈性應(yīng)變,與自由態(tài)納米線彈性應(yīng)變相當(dāng)(圖12d[16])。證實(shí)了“應(yīng)變匹配”的設(shè)計(jì)概念普適于去孿晶基體中的納米線。
圖12 Nb(110)晶面晶格應(yīng)變與施加應(yīng)變的關(guān)系曲線(插圖是Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料拉伸應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變曲線)、在加載過程中B19′-NiTi(001)晶面的衍射強(qiáng)度與二維X射線衍射譜方位角的關(guān)系曲線、在8.7%循環(huán)前后馬氏體態(tài)NiTi基體中孿晶形貌的比較、納米線的彈性應(yīng)變極限與以往文獻(xiàn)報(bào)道的比較[
Fig.12 Evolution of d-spacing strain with respect to applied strain for the Nb (110) plane perpendicular to the wire axial direction during tensile loading (Inset is the macroscopic stress-strain curve of the NICSMA composite) (a), evolution of X-ray diffraction intensity of B19′-NiTi <001> planes versus the azimuth angle during tensile loading (b), TEM micrographs of twin morphologies of the martensitic NiTi matrix before and after a tensile deformation cycle to 8.7% (c), comparison of the elastic strain limits of Nb nanowires embedded in the matrix deforming by dislocation slip (1), Nb nanowires embedded in the matrix deforming by detwinning (2), and some freestanding nanowires (3) (d)[
5.1.1 超大線彈性應(yīng)變Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料絲材 通過化學(xué)成分設(shè)計(jì)與熱處理調(diào)控,獲得的Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料中NiTi基體處于馬氏體狀態(tài)。基于Nb納米線的超大彈性應(yīng)變(圖13a[17],根據(jù)原位拉伸同步輻射測試的衍射峰計(jì)算),以及其與納米尺度馬氏體疇之間的耦合作用,該復(fù)合材料呈現(xiàn)的線彈性應(yīng)變?yōu)?%,遠(yuǎn)高于現(xiàn)有金屬材料;屈服強(qiáng)度為1800 MPa,儲能效率大于96%,遠(yuǎn)超過商業(yè)化NiTi記憶合金(圖13b[17])。
圖13 Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料在加卸載過程中Nb納米線的晶格應(yīng)變隨外加應(yīng)變變化曲線、復(fù)合材料在加載過程中的應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變曲線以及與商業(yè)化NiTi記憶合金的對比[
Fig.13 The d-spacing strain with respect to applied macroscopic strain for the Nb (110) planes perpendicular to the loading direction in the NiTi-Nb composite (a), comparison of tensile stress-strain curves of the composite wire (red curve) and a commercial superelastic NiTi wire (yellow curve) (b)[
5.1.2 高超彈應(yīng)力小滯后Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料 通過化學(xué)成分設(shè)計(jì)、冷拔絲及熱處理調(diào)控,獲得了Nb納米線/納米晶NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料,基于Nb納米線的高強(qiáng)度及其與納米晶NiTi基體之間的耦合作用,使復(fù)合材料呈現(xiàn)的超彈應(yīng)力高達(dá)1.8 GPa,如圖14[18]所示,是普通NiTi記憶合金的3倍;超彈應(yīng)力滯后約為100 MPa,是普通NiTi記憶合金的1/3。
圖14 Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料及其與單體NiTi超彈性曲線的對比[
Fig.14 The tensile cyclic stress-strain curves of the nanostructured Nb reinforced NiTi shape memory alloy composite wire (strain: 4% and 5%); the tensile cyclic stress-strain curve of a commercial superelastic NiTi shape memory alloy wire[
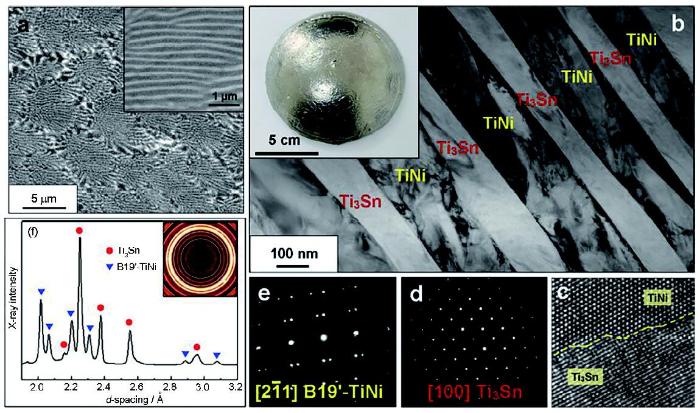
5.1.3 研發(fā)高強(qiáng)高韌Ti3Sn/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料 基于化學(xué)成分設(shè)計(jì)Ti57Ni35Sn8 (原子分?jǐn)?shù),%),通過Ti-Ni-Sn合金的液-固共晶轉(zhuǎn)變,獲得原位自生亞微米尺度TiNi-Ti3Sn片層復(fù)合材料,TiNi和Ti3Sn的片層厚度分別約為300和200 nm (圖15a和b[19])。復(fù)合材料中的TiNi與Ti3Sn相界面結(jié)合良好(圖15c[19]),兩組元的晶體結(jié)構(gòu)分別為D019-Ti3Sn和B19′-TiNi結(jié)構(gòu)(圖15d和f[19])。微觀組織結(jié)構(gòu)觀察結(jié)果和高能X射線測試一致,如圖15f[19]所示。
圖15 Ti3Sn/TiNi復(fù)合材料微觀組織結(jié)構(gòu)[
Fig.15 Typical microstructure of the TiNi-Ti3Sn composite[
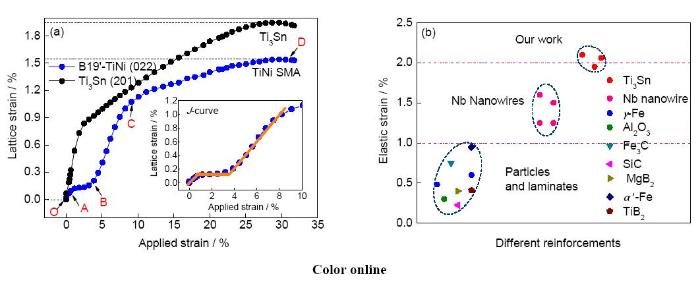
Ti3Sn/TiNi復(fù)合材料在加載過程中,Ti3Sn的彈性應(yīng)變(晶格應(yīng)變,如圖16a[19]所示)在TiNi發(fā)生起始彈性變形和去孿晶變形過程中迅速增加,之后逐漸增加到2%,此彈性應(yīng)變極限是單體Ti3Sn (大約0.3%)的6倍,遠(yuǎn)高于位錯(cuò)滑移基體中各種增強(qiáng)相(納米線、片及顆粒)的彈性應(yīng)變極限(圖16b[19]),說明NiTi基體的馬氏體去孿晶(點(diǎn)陣切變)能使亞微米尺度Ti3Sn呈現(xiàn)大彈性應(yīng)變極限。
圖16 Ti3Sn/TiNi復(fù)合材料變形行為[
Fig.16 Deformation behavior of the TiNi-Ti3Sn composite[
基于馬氏體態(tài)NiTi基體中Ti3Sn呈現(xiàn)大彈性應(yīng)變極限,Ti3Sn/TiNi復(fù)合材料展示的最大壓縮強(qiáng)度高達(dá)3 GPa,斷裂應(yīng)變超過30% (圖17a[19]),此綜合力學(xué)性能遠(yuǎn)超過其它高性能共晶片層復(fù)合材料(圖17b[19])。
圖17 Ti3Sn/TiNi復(fù)合材料的的室溫壓縮應(yīng)力應(yīng)變曲線、復(fù)合材料的力學(xué)性能和其它的高性能金屬基復(fù)合材料對比[
Fig.17 Room-temperature compressive stress-strain curve of the composite (a), comparison of the mechanical properties of our composite with those of other high-performance metal-based lamellar composites in which the soft component is a conventional metal (without the "J-curve" deformation attributes) rather than the biopolymer-like metal ("J-curve" deformation attributes) (b)[
目前,商業(yè)化NiTi記憶合金雙程形狀記憶效應(yīng)的最大缺點(diǎn)是:其在降溫過程中的輸出應(yīng)力很低,在實(shí)際應(yīng)用過程中,需要附加偏置彈簧,從而造成驅(qū)動機(jī)構(gòu)復(fù)雜,并占據(jù)較大空間。
基于NiTi記憶合金中Nb納米線的彈性應(yīng)變極限(6%)遠(yuǎn)大于制造彈簧用鋼的彈性應(yīng)變極限(<0.5%),由于Nb納米線在降溫過程中的驅(qū)動作用,且可大大提高降溫過程中的驅(qū)動應(yīng)力,提高了雙程記憶效應(yīng)的雙驅(qū)動特性。據(jù)此研發(fā)的Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料,在20次升降溫循環(huán)過程中呈現(xiàn)穩(wěn)定的雙程形狀記憶效應(yīng)(圖18[20]),降溫驅(qū)動力是商用NiTi記憶合金的5倍。這相當(dāng)于將Nb納米線偏置彈簧復(fù)合于NiTi記憶合金中,大大簡化了驅(qū)動機(jī)構(gòu),減少了所占據(jù)空間。
圖18 復(fù)合材料絲雙程驅(qū)動特性[
Fig.18 Two-way actuated properties of the composite wire[
此外,基于“應(yīng)變匹配”概念,還研發(fā)了其它高強(qiáng)高韌復(fù)合材料,例如:高強(qiáng)度大機(jī)械滯后的Nb納米線/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料[21];高強(qiáng)高韌的Ti2Ni/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料[22];高強(qiáng)高韌Ti5Si3/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料[23];高強(qiáng)度、大塑性及高阻尼Ti3Sn/NiTi記憶合金原位自生復(fù)合材料[24];高強(qiáng)高塑高熔點(diǎn)金屬W/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料[25,26,27]。
彈性應(yīng)變工程是近年來國際上新興的研究領(lǐng)域,其基本原理是:采用彈性應(yīng)變改變晶體材料的電子結(jié)構(gòu)從而調(diào)控其物理與化學(xué)性能。彈性應(yīng)變工程已在超導(dǎo)、磁性、吸附、催化等領(lǐng)域取得重要突破。然而,金屬材料的彈性應(yīng)變極限較小(<0.5%),且難以在無外載下保持大彈性應(yīng)變。因此,該領(lǐng)域的關(guān)鍵問題是如何使晶體材料保持大彈性應(yīng)變。本工作基于點(diǎn)陣切變基體中納米線(或表面納米膜)呈現(xiàn)大彈性應(yīng)變,以及兩者之間的應(yīng)力耦合作用,提高了復(fù)合材料的物理與化學(xué)性能。
5.3.1 提高Nb納米線/NiTi基體復(fù)合材料的超導(dǎo)溫度 如前所述,若Nb納米線與馬氏體態(tài)NiTi基體構(gòu)成復(fù)合材料,在后者發(fā)生馬氏體去孿晶的過程中,前者的彈性應(yīng)變極限為4%~6%,遠(yuǎn)高于后者的彈性應(yīng)變極限(約0.5%),則可認(rèn)為,在此復(fù)合材料經(jīng)歷加載-卸載后,納米線處于拉應(yīng)變狀態(tài),而NiTi基體處于壓應(yīng)變狀態(tài),從而實(shí)現(xiàn)了在無外載情況下,復(fù)合材料中的納米線保持拉應(yīng)變。
若Nb納米線與母相態(tài)NiTi基體構(gòu)成復(fù)合材料,在后者發(fā)生應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體的過程中,前者的彈性應(yīng)變極限為6%,小于后者的應(yīng)力誘發(fā)馬氏體逆相變應(yīng)變(約8%),則可認(rèn)為,在復(fù)合材料經(jīng)歷加載-卸載后,納米線承受壓應(yīng)變,而NiTi基體承受拉應(yīng)變,從而實(shí)現(xiàn)了在無外載下,復(fù)合材料中的納米線保持壓應(yīng)變。
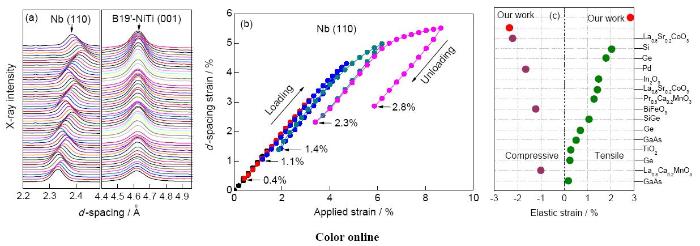
圖19a[16]是馬氏體態(tài)NiTi基體與Nb納米線在拉伸循環(huán)過程中的一維高能XRD譜,經(jīng)Nb (110)面間距計(jì)算可得,經(jīng)不同應(yīng)變加、卸載后,Nb納米線保留不同的彈性應(yīng)變,最大可達(dá)2.8% (圖19b[16])。此復(fù)合材料中批量納米線的彈性應(yīng)變大于文獻(xiàn)報(bào)道的彈性應(yīng)變(圖19c[16]),解決了長期困擾材料科學(xué)家的“大塊金屬材料大彈性應(yīng)變難以保留與調(diào)控”的難題,可望促進(jìn)彈性應(yīng)變工程領(lǐng)域發(fā)展[16]。
圖19 Nb納米線/NiTi復(fù)合材料在拉伸循環(huán)過程中的一維高能XRD譜、NiTi基體中Nb納米線被保留彈性應(yīng)變與拉伸應(yīng)變的曲線、NiTi基體中Nb納米線被保留拉伸和壓縮彈性應(yīng)變與文獻(xiàn)報(bào)道的基材表面薄膜被保留拉伸和壓縮彈性應(yīng)變的比較[
Fig.19 Evolution of high-energy X-ray diffraction peaks for Nb (110) and B19′-NiTi (001) planes through the multiple-step tensile cycles (a), evolution of d-spacing strain with respect to applied strain for the Nb (110) plane perpendicular to the wire axial direction during the multiple-step tensile cycles (b), comparison of the retained tensile and compressive elastic strains of large quantity Nb nanowires in the composite without external load and those of the reported thin films on substrates and embedded nanoinclusions in films (c)[
5.3.2 提高NiTi合金表面Pt納米膜的電催化性能 采用磁控濺射方法在NiTi記憶合金表面制備Pt納米膜,利用NiTi記憶合金基底的雙程形狀記憶效應(yīng)使Pt納米膜保持拉、壓彈性應(yīng)變,以調(diào)控Pt納米膜的電催化氧還原活性。實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果表明,NiTi記憶合金基底使Pt納米膜(厚度為5 nm)保持1.93%的壓縮應(yīng)變,提高其電催化性能高達(dá)52%,如圖20[28]所示。
圖20 不同應(yīng)變狀態(tài)的10 nm Pt和5 nm Pt納米膜的氧還原反應(yīng)(ORR)線性伏安掃描(LSV)曲線對比[
Fig.20 Polarization curves of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) of 10 and 5 nm Pt nanofilm under different strain states at a scan rate of 0.3 V/s. The data of 10 nm Pt nanofilm are shown with standard deviation[
此外,還研發(fā)了提高物理與化學(xué)性能的表面納米膜/形狀記憶合金復(fù)合材料,例如:(1) 表面FePt納米膜/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料,利用NiTi基底的形狀記憶效應(yīng)對FePt納米膜施加壓應(yīng)變而提高其磁學(xué)性能[29,30];(2) 表面半導(dǎo)體納米膜/FeNiCoTi合金復(fù)合材料,利用FeNiCoTi基底的馬氏體相變浮凸,對其表面半導(dǎo)體納米膜施加拉應(yīng)變,從而提高其光催化活性[31];(3) 表面TiO2納米膜/TiNiNb記憶合金復(fù)合材料,利用TiNiNb記憶合金的雙程記憶效應(yīng)對其表面TiO2納米膜施加彈性應(yīng)變,而縮小其能帶寬度[32];(4) 表面TiO2納米膜/FeNiCoTi合金復(fù)合材料,利用FeNiCoTi基底的馬氏體相變浮凸,對其表面TiO2納米膜施加拉應(yīng)變,從而提高其光催化性能[33]。
基于金屬基體中的位錯(cuò)與納米線交互作用而導(dǎo)致納米線不能體現(xiàn)超常力學(xué)性能的猜測,提出采用點(diǎn)陣切變(如馬氏體相變或去孿晶)型金屬基體的切變應(yīng)變與納米線的彈性應(yīng)變相匹配的設(shè)計(jì)概念,實(shí)現(xiàn)了大塊復(fù)合材料中納米線(帶、粒子)的超常力學(xué)性能(超大彈性應(yīng)變或超高強(qiáng)度),使納米線的超常力學(xué)性能從納米走向宏觀。此突破還引發(fā)了復(fù)合材料組元間的強(qiáng)應(yīng)力耦合效應(yīng),據(jù)此設(shè)計(jì)的納米線Nb/NiTi記憶合金復(fù)合材料兼具大彈性應(yīng)變極限、低彈性模量、高屈服強(qiáng)度,填補(bǔ)了三大類工程材料(金屬、陶瓷及高分子)力學(xué)性能的空白區(qū)。
在金屬結(jié)構(gòu)材料領(lǐng)域,由于納米線具有超大彈性應(yīng)變或超高強(qiáng)度等超常力學(xué)性能,其作為增強(qiáng)劑的大塊金屬基復(fù)合材料曾被期望具有超常力學(xué)性能,然而,納米線的超常力學(xué)性能難以在位錯(cuò)滑移基體中再現(xiàn)。同時(shí),在彈性應(yīng)變工程領(lǐng)域,人們曾期望利用納米線的超大彈性應(yīng)變實(shí)現(xiàn)超常物理與化學(xué)性能,然而,難以實(shí)現(xiàn)公斤級納米線呈現(xiàn)超常物理與化學(xué)性能。本文綜述的基體點(diǎn)陣切變應(yīng)變與納米線彈性應(yīng)變相匹配的設(shè)計(jì)概念,不僅使大塊納米線增強(qiáng)金屬基復(fù)合材料具有超常力學(xué)性能,還可望使公斤級納米線呈現(xiàn)超常的物理與化學(xué)性能。因此,應(yīng)變匹配的設(shè)計(jì)概念值得材料科技工作者關(guān)注,其不僅促進(jìn)高性能金屬基復(fù)合材料的研究進(jìn)展,也對彈性應(yīng)變工程領(lǐng)域研究具有促進(jìn)作用。
1 應(yīng)變匹配概念的提出及證實(shí)


(a) a coil of composite wire with a diameter of 0.5 mm
(b) scanning TEM image of the cross section of composite wire (bright regions, cross sections of Nb nanowires; dark regions, NiTi matrix)
(c) TEM image of a longitudinal section of composite wire (NW indicates nanowire)
(d) macroscopic appearance of a bundle of freestanding Nb nanowires
(e, f) SEM images of the freestanding Nb nanowires

2 相變基體中納米線超大彈性變形的特異性
3 相變基體中納米線彈性變形行為的TEM觀察

(a, b) SAED patterns of longitudinal view of the two samples(c, d) TEM bright field images of the two samples corresponding to Figs.8a and b(e, f) HAADF images of the two sample(g, h) HRTEM image revealing the interfaces between a Nb nanowire and NiTi matrix

(a) bright feld image of a microbeam fabricated by means of focus ion beam milling(b) enlarged view of a Nb nanowire in the beam(c) HRTEM image of the region marked as c in 
4 應(yīng)變匹配概念的普適性
4.1 普適于納米帶

4.2 普適于納米粒子
4.3 普適于去孿晶基體

5 利用應(yīng)變匹配概念研發(fā)高性能復(fù)合材料
5.1 指導(dǎo)研發(fā)高力學(xué)性能復(fù)合材料


(a) SEM backscattered electron images of the composite. The inset shows the Ti3Sn (light)-TiNi (dark) lamellar structure at high magnification
(b) TEM bright-field image of the composite. The inset shows the button ingot of the composite
(c) HRTEM image of the interface between TiNi and Ti3Sn
(d, e) display selected-area electron diffraction patterns of the Ti3Sn and TiNi lamellae, respectively, shown in
(f) one-dimensional high-energy X-ray diffraction (HE-XRD) pattern of the composite. The inset contains its corresponding two-dimensional HE-XRD pattern
(a) the lattice strain evolutions of B19'-TiNi (022) and Ti3Sn (201) planes perpendicular to the loading direction as a function of the applied macroscopic strain. The inset shows an enlarged view of the lattice strain curve of the TiNi in the initial stages of deformation
(b) the comparison of the elastic strains of Ti3Sn achieved in our composite with different reinforcements (such as nanowires, laminates, and particles) embedded in conventional metal matrices, which are deformed by dislocation slip

5.2 提高NiTi記憶合金的雙程驅(qū)動特性

(a) output strain-temperature curve of the composite without external load
(b) evolution of d-spacing strain with respect to temperature for the Nb (110) plane perpendicular to the wire axial direction
5.3 指導(dǎo)研發(fā)優(yōu)異物理與化學(xué)性能的復(fù)合材料

6 結(jié)論與展望
來源--金屬學(xué)報(bào)
“推薦閱讀”
【責(zé)任編輯】:國檢檢測版權(quán)所有:轉(zhuǎn)載請注明出處







 滬公網(wǎng)安備31011202020290號
滬公網(wǎng)安備31011202020290號
